Docker Tutorial
What is Docker and Why
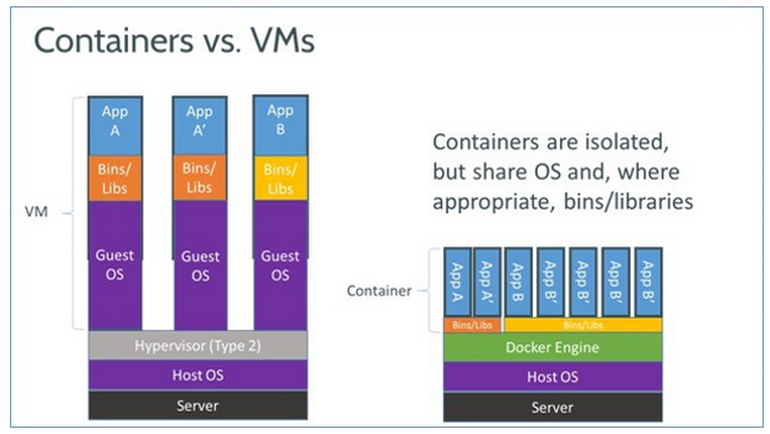
Docker is a tool to create, deploy, and run applications without any fallbacks about different production environment.it’s a bit like VM but unlike it, you can see the difference between Docker and VM in below image.
Container runs on Host os but VM run in separate OS and waste your resource.
How to install Docker on linux
Update the apt package index:
sudo apt-get update
Install packages to allow apt to use a repository over HTTPS
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
Add Docker’s official GPG key:
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-key fingerprint 0EBFCD88
get last version from repository
sudo add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
update and install
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce
Create docker image
create Dockerfile
Each docker file is a script to creating the image
FROM : define base image like ubuntu
MAINTAINER : declare the author
RUN : it takes to command and run it .it used to build image . For example install, its run during the build time
CMD : used for executing a specific command, it uses for initial, default command that gets executed and run command not in during build time
ENTRYPOINT : the first command executed after creating image
Add : get two arguments, source, and destination, copy from host to container if the source is URL its download from the web
ENV : declate environemt variable example # Usage: ENV key value
WORKDIR : set working directory for CMD Command
EXPOSE : The EXPOSE command is used to associate a specified port to enable networking between the running process inside the container and the outside world
VOLUME : create volume for container
example create Dockerfile
FROM openjdk:8u171-jre-alpine3.8
ADD target/myApp.jar myApp.jar
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/myApp.jar"]
EXPOSE 8085
then you can create localy image
docker build --tag=myappco:1 .
run docker image
docker run --name=config-server --publish=8086:8085 myappco:1
port 8086 is external port -it – enable interactive mode -d – detach from the container after booting
if you have multi app and they work together you should create a network for them or create link between them
Docker stages
create automation for create java app , you can use stage to create automation for create java application we use openjdk:8-jre-alpine for image becuase it’s smallest image
Example for create stage
FROM alpine/git as clone
WORKDIR /app
RUN git clone https://github.com/rasoulpoordelan/dockerTestAutomation.git
FROM maven:3.5.4-jdk-8-alpine as build
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=clone /app/dockerTestAutomation /app
RUN mvn clean package
FROM openjdk:8-jre-alpine
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=build /app/target/myapp.jar /app
EXPOSE 8080
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/app/myapp.jar"]
Network
Network is one of most challenging skill on the docker we have two type network in docker single host and cluster. by default, docker container connects to the default network in the same host and can be accessed from that host and IP. you can create your own network for your application work together and find each other with the name on the network. we have a bridge network in the same host and overlay network for the cluster. every container in default bridge can connect each other with IP but in user definition network they can find each other by name and all ports are accessible.
Create new network and connect to that
docker network create my-net
docker network connect my-net my-app
create a bridge network
docker network create -d bridge mynet
create an overlay network for use with swarm services, use a command like the following:
docker network create -d overlay my-overlay
To create an overlay network which can be used by swarm services or standalone containers to communicate with other standalone containers running on other Docker daemons, add the –attachable flag:
docker network create -d overlay --attachable my-attachable-overlay
Get network list
docker network ls
Inspecting a Docker network
docker network inspect networkname
Docker volume
With Docker volume we can manage our data within Docker continer.continer have space to save your data but when you remove it all data in continer is removed and the other hand you can use it for share data between continer.
best way : use –mount insted of -v or volume to assign to continer
create volume
docker create volume myvol
show volume
docker volume inspect myvol
assign to continer
$ docker run -d --name devtest --mount source=myvol,target=/app nginx:latest
If you start a container which creates a new volume, as above, and the container has files or directories in the directory to be mounted (such as /app/ above), the directory’s contents are copied into the volume. The container then mounts and uses the volume, and other containers which use the volume also have access to the pre-populated content.
Docker Compose
ocker Compose is used to run multiple containers as a single service, for example, you have application have dependencies to NGINX and Postgress you can create a compose file to create them as service. Docker Compose is a YAML File docker-compose.yml. you can create it with any editor. Docker Compose have version
The directory structure will look like this:
simple_app
├── content
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ └── code
│ ├── simple_app.py
│ └── requirements.txt
└── docker-compose.yml
Three steps to using Docker Compose
- define each service in a Docker file
- define the services and their relation on YAML file
- docker-compose up
Build Image (if an appropiated dockerfile is existed)
docker-compose build
Scale Running containers
docker-compose scale SERVICE=3
all command existed
build Build or rebuild services
kill Kill containers
help Get help on a command
logs View output from containers
port Print the public port for a port binding
ps List containers
pull Pulls service images
rm Remove stopped containers
run Run a one-off command
scale Set number of containers for a service
start Start services
stop Stop services
restart Restart services
up Create and start containers
create a simple compose
we have frontend from Redis Commander and connected that to Redis
it’s our YAML file
backend:
image: redis:3
restart: always
frontend:
build: commander
links:
- backend:redis
ports:
- 8090:8081
environment:
- VAR1=value
restart: always
the run it
docker-compose up -d
it’s run a command like this
docker build -t commander commander
docker run -d --name frontend -e VAR1=value -p 8090:8081
--link backend:redis commander
docker-compose up -d builds images if needed. docker-compose ps shows running containers. docker-compose stop stop services
Docker Swarm
Docker have natively swarm mode for managing a cluster of Dockers.
preperation
create master swarm(first node)
docker swarm init --advertise-addr MANAGER_IP
for getting a token to join
docker swarm join-token worker
docker swarm join-token manager
joining to swarm use the above code to join to swarm
How to create and manage service
docker service create --replicas 5 -p 80:80 --name web myApp
get service status
docker service ls
get specific service status
docker service ps myApp
change scale service
docker service scale myApp=8
applying rolling update
docker service update --image <imagename>:<version> myApp
remove service
docker service rm web
get nodes
get the specification of the node
docker node inspect [worker1 | self]
for getting node
docker node ls
Create a stack
when running Docker in swarm mode you can use Docker Stack deploy to deploy a complete application to the swarm deploy accept a type of compose file.
Create Example Application
Voting app For this application we will use the Docker Example Voting App. This app consists of five components:
Python webapp which lets you vote between two options Redis queue which collects new votes .NET worker which consumes votes and stores them in Postgres database backed by a Docker volume Node.js webapp which shows the results of the voting in real time.
create docker-stack.yml
version: "3"
services:
redis:
image: redis:alpine
ports:
- "6379"
networks:
- frontend
deploy:
replicas: 2
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
db:
image: postgres:9.4
volumes:
- db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
- backend
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
vote:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_vote:before
ports:
- 5000:80
networks:
- frontend
depends_on:
- redis
deploy:
replicas: 2
update_config:
parallelism: 2
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
result:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_result:before
ports:
- 5001:80
networks:
- backend
depends_on:
- db
deploy:
replicas: 1
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
worker:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_worker
networks:
- frontend
- backend
deploy:
mode: replicated
replicas: 1
labels: [APP=VOTING]
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
delay: 10s
max_attempts: 3
window: 120s
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
visualizer:
image: manomarks/visualizer
ports:
- "8080:8080"
stop_grace_period: 1m30s
volumes:
- "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
networks:
frontend:
backend:
volumes:
db-data:
create stack
docker stack deploy --compose-file docker-stack.yml vote
create Dockerfile in compose
version: '3'
services:
webapp:
build:
context: ./dir
dockerfile: Dockerfile-alternate
args:
buildno: 1
Create docker registry
you can get it from docker hub
docker run -d -p 50000:5000 --restart always --name my-registry registry:latest
for send register to our registry we should tag it and push it to the registry
docker tag app:latest my-registry:50000/app:latest
docker push my-registry:50000/app
in the browser you can see it http://localhost:50000/v2/_catalog
when you want to use it you should add the address in insecure
/etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"insecure-registries" : [ "hostname.cloudapp.net:5000" ]
}
reload docker
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
Cheat sheet
Docker build
docker build [options] . -t "app/container_name" # name
Docker run
docker run [options] IMAGE # see `docker create` for options
example
docker run -it --name=myname myappImage
-it interactive -d detached
-p 8080:8080
Create continer from image
docker create [options] IMAGE
-a, --attach # attach stdout/err
-i, --interactive # attach stdin (interactive)
-t, --tty # pseudo-tty
--name NAME # name your image
-p, --publish 5000:5000 # port map
--expose 5432 # expose a port to linked containers
-P, --publish-all # publish all ports
--link container:alias # linking
-v, --volume `pwd`:/app # mount (absolute paths needed)
-e, --env NAME=hello # env vars
example
docker create --name app_redis_1 \
--expose 6379 \
redis:4
Run command in continer
docker exec [options] CONTAINER COMMAND
-d, --detach # run in background
-i, --interactive # stdin
-t, --tty # interactive
example
docker exec app_web_1 tail logs/development.log
docker exec -t -i app_web_1 rails c
Docker start/stop contianer
docker start [options] CONTAINER
-a, --attach # attach stdout/err
-i, --interactive # attach stdin
docker stop [options] CONTAINER
Manage continer
docker ps
docker ps -a
docker kill $ID
Docker images
docker images # show images
docker images -a # also show intermediate
docker rmi b750fe78269d